Java 8에서 도입된 개념.
"단 하나의 추상 메서드를 가지는 인터페이스"
함수형 인터페이스의 경우 람다식을 통해 객체를 생성하거나 제어할 수 있음.
함수형 인터페이스의 특징
- 단일 추상 메서드: 함수형 인터페이스는 하나의 추상 메서드를 정의해야 함.
- 람다식 지원: 함수형 인터페이스를 통해 람다식 사용 가능
- @FunctionalInterface 어노테이션: 함수형 인터페이스라는 것을 명시적으로 나타내기 위해, @FunctionalInterface 어노테이션을 사용할 수 있음. 선택사항이나 인터페이스가 하나의 추상메서드만 가지도록 강제하는 역할
@FunctionalInterface
interface MyFunctionalInterface {
void myMethod();
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 기존 익명 클래스 방식
MyFunctionalInterface myInterface = new MyFunctionalInterface() {
@Override
public void myMethod() {
System.out.println("This is a lambda expression.");
}
}
// 람다식을 사용하여 함수형 인터페이스 구현
MyFunctionalInterface myInterface = () -> {
System.out.println("This is a lambda expression.");
};
myInterface.myMethod(); // "This is a lambda expression." 출력
}
}
Java8에서 제공하는 주요 함수형 인터페이스
Predicate<T>
T타입의 파라미터를 받아 조건을 평가하고 true/false를 반환하는 함수형 인터페이스
Predicate<Integer> isPositive = x -> x > 0;
System.out.println(isPositive.test(5)); // true
Function<T,R>
T타입의 파라미터를 받아 R타입을 반환
Function<String, Integer> stringLength = s -> s.length();
System.out.println(stringLength.apply("Hello")); // 5
Consumer<T>
T타입의 파라미터를 받아 처리만 함. (반환하지 않음)
Consumer<String> printMessage = message -> System.out.println(message);
printMessage.accept("Hello, World!"); // "Hello, World!" 출력
Supplier<T>
파라미터 없이 T타입을 반환
Supplier<String> messageSupplier = () -> "Hello from Supplier!";
System.out.println(messageSupplier.get()); // "Hello from Supplier!"
BinaryOperator<T>
2개의 T타입을 입력받아 T타입을 반환
BinaryOperator<Integer> add = (a, b) -> a + b;
System.out.println(add.apply(2, 3)); // 5
BiFunction<T,U,R>
T,U 타입을 받아 R타입을 반환
BiFunction<Integer, Integer, String> concatenate = (a, b) -> a + " and " + b;
System.out.println(concatenate.apply(5, 10)); // "5 and 10"
@FunctionalInterface 어노테이션
어노테이션을 추가하면 해당 인터페이스가 함수형 인터페이스임을 명시적으로 나타낸다. 이를 통해 실수로 여러 추상 메서드를 추가하는 것을 방지할 수 있다고 한다.
예를 들어, 2개의 추상 메서드를 정의하면 컴파일 오류가 발생한다고 한다.
@FunctionalInterface
interface MyAnotherFunctionalInterface {
void singleAbstractMethod();
// default 메서드는 여러 개 있어도 상관 없음
default void defaultMethod() {
System.out.println("This is a default method.");
}
}
Collection의 정렬 예시
Collection에서 정렬할 때 유용하게 사용할 수 있다.
아래처럼 Person 클래스가 있다.
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
그리고 Collection 에는 sort 메서드가 있는데 파라미터로 Comparator를 추가로 받을 수 있다.
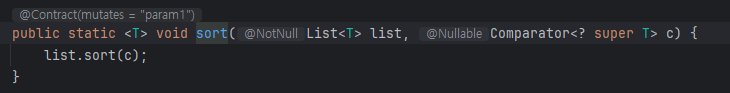
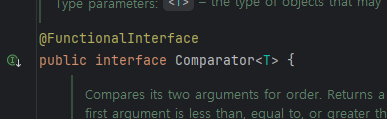
Comparator는 함수형 인터페이스이다.
person을 나이순으로 정렬한다고 할 때 익명 클래스로 구현하면 아래와 같다.
List<Person> persons = new ArrayList<>(List.of(person2, person1));
persons.sort(new Comparator<Person>() {
@Override
public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {
if (o1.getAge() < o2.getAge()) {
return -1;
} else if (o1.getAge() > o2.getAge()) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
});
하지만 람다식을 쓰면 아래와 같이 줄일 수 있다.
persons.sort((o1, o2) -> {
if (o1.getAge() < o2.getAge()) {
return -1;
} else if (o1.getAge() > o2.getAge()) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
});
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 원시 자료형 (Primitive Type) 과 참조 자료형 (Reference Type) (0) | 2024.10.03 |
|---|---|
| Java가 빌드되고 실행되는 과정 (3) | 2024.10.03 |
| 제네릭 (Generic) 에 대해 (1) | 2024.10.03 |
| Java의 주요 특징 (1) | 2024.10.03 |
| OpenFeign 알아보기 (1) | 2024.08.30 |